1424 Diagonal Traverse II - Medium
Problem:
Given a 2D integer array nums, return all elements of nums in diagonal order as shown in the below images.
Example 1:
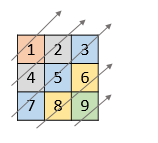
Input: nums = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] Output: [1,4,2,7,5,3,8,6,9]
Example 2:
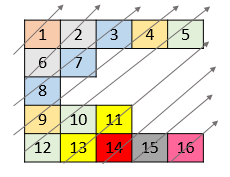
Input: nums = [[1,2,3,4,5],[6,7],[8],[9,10,11],[12,13,14,15,16]] Output: [1,6,2,8,7,3,9,4,12,10,5,13,11,14,15,16]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= nums[i].length <= 1051 <= sum(nums[i].length) <= 1051 <= nums[i][j] <= 105
Problem Analysis:
The high-level strategy of this solution is to traverse the given 2D matrix (nums) and organize its elements into lists based on their diagonal index (i+j). The algorithm uses a list m to store these diagonally organized lists. The outer loop iterates over each row of the matrix, and the inner loop iterates over each element in the row. For each element, the algorithm determines its diagonal index (i+j) and appends the element to the corresponding list in m. Finally, the algorithm flattens the lists in reverse order to get the result.
-
Time Complexity:
- The nested loops iterate over each element in the 2D matrix once.
- Inside the loop, the operation of appending elements to the appropriate diagonal list takes constant time.
- Therefore, the overall time complexity is O(m * n), where m is the number of rows and n is the number of columns in the matrix.
-
Space Complexity:
- The space complexity is primarily determined by the auxiliary list
mused to store the diagonally organized lists. - In the worst case, all elements could belong to different diagonals, resulting in O(m + n) diagonally organized lists.
- The space complexity is O(m + n) to store these lists.
- Additionally, the output list has space complexity O(m * n) since it contains all elements from the matrix.
- Therefore, the overall space complexity is O(m + n + m * n), which simplifies to O(m * n).
- The space complexity is primarily determined by the auxiliary list
Solutions:
class Solution:
def findDiagonalOrder(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
m = []
for i, row in enumerate(nums):
for j, v in enumerate(row):
if i+j >= len(m):
m.append([])
m[i+j].append(v)
return [v for d in m for v in reversed(d)]
 Walter Teng.
Walter Teng.