2 Add Two Numbers - Medium
Problem:
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order, and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example 1:
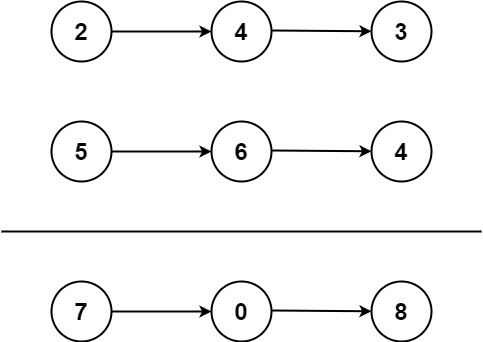
Input: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] Output: [7,0,8] Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.
Example 2:
Input: l1 = [0], l2 = [0] Output: [0]
Example 3:
Input: l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9] Output: [8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each linked list is in the range
[1, 100]. 0 <= Node.val <= 9- It is guaranteed that the list represents a number that does not have leading zeros.
Problem Analysis:
- Initialize: Create a dummy node and a current pointer (
cur) to keep track of the current position in the result linked list. - Traverse and Add: Iterate through both linked lists (
l1andl2) and add corresponding node values along with any carry from the previous addition. - Update Carry and Value: Calculate the sum (
val), update the carry, and create a new node with the result value. Move the current pointer to the next position. - Handle Unequal Lengths: Continue the process until you reach the end of both lists. If one list is shorter than the other, use 0 for missing values.
- Return Result: Return the next node of the dummy node, which contains the result linked list.
Be Careful of Edge Cases
-
Carry at the End: If there is a carry after processing all the nodes, an additional node needs to be added to represent the carry.
-
Different Lengths: The code handles cases where
l1andl2have different lengths by assigning 0 to the value of the missing node in the shorter list.
Complexity
- Time Complexity: O(max(N, M)), where N and M are the lengths of the input linked lists
l1andl2. The algorithm processes each node once. - Space Complexity: O(max(N, M)), the space required for the output linked list.
Solutions:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy = ListNode()
cur = dummy
carry = 0
# edge case where carry exist but no existing node in front eg. 7 + 8
while l1 or l2 or carry:
# init empty node for unequal pair
v1 = l1.val if l1 else 0
v2 = l2.val if l2 else 0
val = v1 + v2 + carry
carry = val // 10
val = val % 10
cur.next = ListNode(val)
# increment
cur = cur.next
l1 = l1.next if l1 else None
l2 = l2.next if l2 else None
return dummy.next
- [ ]
 Walter Teng.
Walter Teng.